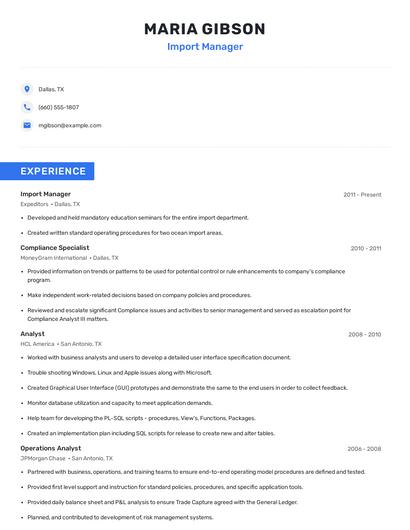
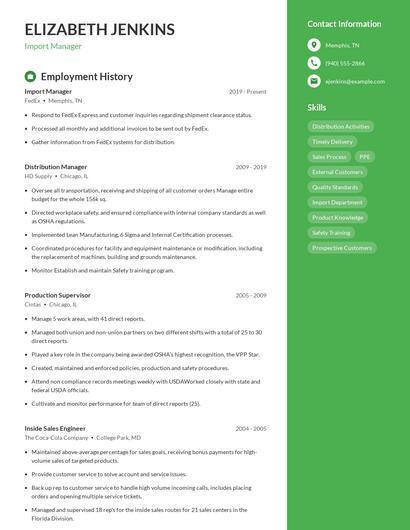
What does an import manager do?
Import manager responsibilities
Here are examples of responsibilities from real import manager resumes:
- Support EDI technology system to manage essential company data.
- Negotiate letters-of-credit with suppliers and manage customs brokers and forwarders.
- Work in compliance with multiple shipping companies and freight forwarders to ensure their containers make their arrival time.
- Handle the branch s largest pharmaceutical account with minimal rejects by utilizing a working knowledge of FDA and CBP regulations.
- File various declarations with BATF/TTB, USCBP, and USDA.
- Coordinate all customs and FDA clearance.
- Resolve problems quickly with U.S. Customs and FDA.
- Aid clients with the creation of HTS classification databases.
- Transmit and prepare the ACH statement to pay customs duties.
- Implement process and procedures for FTZ use and FTA savings.
- Audit 7501 and billing invoices for accuracy and paid ACH statements.
- Check HTS codes for products and request binding rulings from customs if necessary.
- Create an inter-departmental team to determine which ERP and WMS system to implement.
- Determine ocean and inland sell rates to all destinations for LCL and FCL freight.
- File timely export declarations with AES for Japanese issue carnets for development tool consoles.
Import manager skills and personality traits
We calculated that 19% of Import Managers are proficient in Customer Service, Logistics, and Forwarders. They’re also known for soft skills such as Communication skills, Leadership skills, and Management skills.
We break down the percentage of Import Managers that have these skills listed on their resume here:
- Customer Service, 19%
Defined and implemented long and short-term objectives; policy implementation, advertising / promotions, merchandising and customer service.
- Logistics, 11%
Managed staff of Import Analysts and Traffic Coordinators in accomplishing day-to-day logistics responsibilities for international and domestic shipments.
- Forwarders, 6%
Negotiated letters-of-credit with suppliers and managed customs brokers and forwarders.
- Customs Compliance, 5%
Developed and implemented all in-house Customs compliance.
- Freight Forwarders, 5%
Manage freight forwarders/UPS (audio/LiDar) rate/lane country specific based.
- Customs Brokers, 5%
Determined Tariff Classifications and rated commercial invoices before forwarding all necessary documents to Customs Brokers for clearance.
Most import managers use their skills in "customer service," "logistics," and "forwarders" to do their jobs. You can find more detail on essential import manager responsibilities here:
Communication skills. One of the key soft skills for an import manager to have is communication skills. You can see how this relates to what import managers do because "top executives must be able to convey information clearly and persuasively." Additionally, an import manager resume shows how import managers use communication skills: "maintained daily communication with distribution centers toward prioritizing incoming cargo and rapidly troubleshooting critical concerns. "
Leadership skills. Another essential skill to perform import manager duties is leadership skills. Import managers responsibilities require that "top executives must be able to shape and direct an organization by coordinating policies, people, and resources." Import managers also use leadership skills in their role according to a real resume snippet: "provide strategic and tactical leadership in management of nike's north america customs compliance and duty management program. "
Problem-solving skills. A big part of what import managers do relies on "problem-solving skills." You can see how essential it is to import manager responsibilities because "top executives need to identify and resolve issues within an organization." Here's an example of how this skill is used from a resume that represents typical import manager tasks: "resolved problems quickly with u.s. customs and fda. "
Time-management skills. Another common skill required for import manager responsibilities is "time-management skills." This skill comes up in the duties of import managers all the time, as "top executives do many tasks concurrently to ensure that their work gets done and that the organization meets its goals." An excerpt from a real import manager resume shows how this skill is central to what an import manager does: "air imports to meet special promotions and in store deadlines. "
The three companies that hire the most import managers are:
- Yusen Logistics11 import managers jobs
- Expeditors2 import managers jobs
- Air Express International Usa Inc1 import managers jobs
Choose from 10+ customizable import manager resume templates
Build a professional import manager resume in minutes. Our AI resume writing assistant will guide you through every step of the process, and you can choose from 10+ resume templates to create your import manager resume.Compare different import managers
Import manager vs. Manager/partner
A manager/partner or managing partner is an individual who manages the daily activities of a company as well as guides its overall strategic business direction. Managing partners must cooperate with other executives, board members, and employees to implement organizational goals, procedures, and policies. They are responsible for the hiring and managing of employees and should follow the executive committee guidelines and federal and state laws and regulations. Managing partners must also maintain positive client relationships and lead the drive for new business acquisitions.
While similarities exist, there are also some differences between import managers and manager/partner. For instance, import manager responsibilities require skills such as "logistics," "forwarders," "customs compliance," and "freight forwarders." Whereas a manager/partner is skilled in "business development," "project management," "client facing," and "account management." This is part of what separates the two careers.
Managers/partner tend to reach similar levels of education than import managers. In fact, managers/partner are 1.4% more likely to graduate with a Master's Degree and 1.3% more likely to have a Doctoral Degree.Import manager vs. Director/manager
A director/manager is responsible for developing strategic techniques to boost the operational efficiency of an organization in delivering high-quality services and satisfaction for the customers and business clients. Directors/managers identify business opportunities that would support the company's long-term goals and objectives, generating more revenues and closing contract deals for the business. They also handle the departmental budgets, allocating adequate resources for operations and project management. A director/manager must have excellent communication and leadership skills, especially in overseeing staff performance and handling their concerns.
Each career also uses different skills, according to real import manager resumes. While import manager responsibilities can utilize skills like "logistics," "forwarders," "customs compliance," and "freight forwarders," director/managers use skills like "healthcare," "patients," "home health," and "oversight."
Director/managers earn a higher average salary than import managers. But director/managers earn the highest pay in the technology industry, with an average salary of $131,566. Additionally, import managers earn the highest salaries in the technology with average pay of $69,694 annually.Average education levels between the two professions vary. Director/managers tend to reach similar levels of education than import managers. In fact, they're 1.2% more likely to graduate with a Master's Degree and 1.3% more likely to earn a Doctoral Degree.Import manager vs. Line manager
As line managers, they oversee other employees and the business operations while reporting to a higher manager. They play a significant role in the operation of the business from supervising and managing workers daily and acting as a link to upper management and employees. It is part of their responsibility to recruit and hire talent to fill team positions, provide training and learning to new hires, and ensuring that the employees are doing their jobs effectively and efficiently.
The required skills of the two careers differ considerably. For example, import managers are more likely to have skills like "customer service," "logistics," "forwarders," and "customs compliance." But a line manager is more likely to have skills like "client facing," "continuous improvement," "service line," and "customer satisfaction."
When it comes to education, line managers tend to earn similar degree levels compared to import managers. In fact, they're 3.7% less likely to earn a Master's Degree, and 0.1% less likely to graduate with a Doctoral Degree.Import manager vs. Lead manager
A lead manager is primarily in charge of overseeing the progress of a particular office or department. Although the responsibilities will vary depending on their industry, it will typically revolve around producing progress reports, reviewing documentation and transactions, managing the budget, procuring supplies, and devising strategies to generate leads and reach goals faster. Furthermore, as a lead manager, it is essential to spearhead projects and encourage staff, all while implementing the company's policies and regulations.
Types of import manager
Updated January 8, 2025