Average Restaurant Profit Margin Overview (2026): The success of a restaurant hinges on achieving a healthy profit margin, where the revenue generated by guests exceeds all operational costs. While this may sound straightforward, many restaurants operate on very thin margins.
If you’re a restaurateur interested in the current average restaurant profit margins, or simply a curious diner, we have the insights you need. Our analysis of the U.S. restaurant industry reveals:
-
The average profit margin for full-service restaurants ranges from 3-5%.
-
The average profit margin for quick-service restaurants falls between 6-9%.
-
Fast-food establishments and bars boast the highest average profit margins.
Profit Margins by Restaurant Type
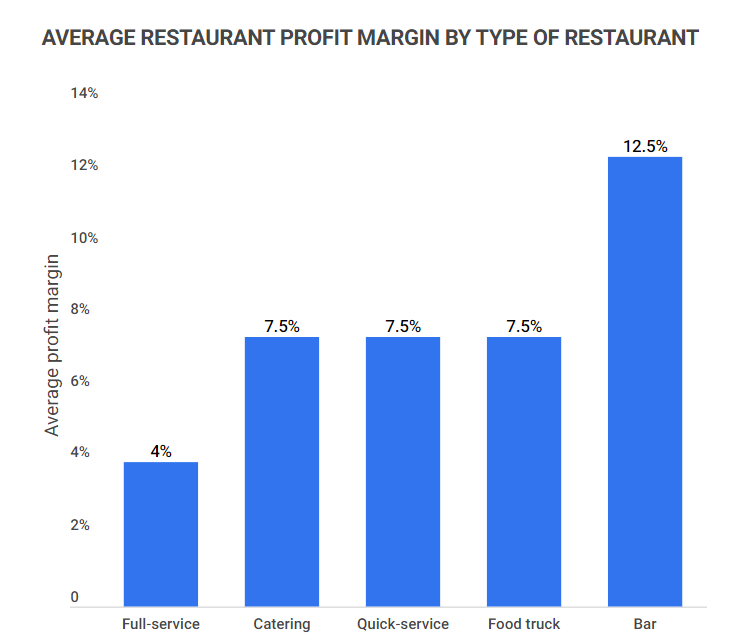
Average restaurant profit margins can vary significantly, generally falling between 0-15%, depending on the restaurant type. Full-service restaurants generally incur higher operational costs compared to quick-service or food trucks.
Below is a detailed breakdown of average restaurant profit margins by type:
Average Restaurant Profit Margin by Type
| Restaurant Type | Average Profit Margin |
|---|---|
| Full-service restaurant | 3-5% |
| Quick-service restaurant | 6-9% |
| Bar | 10-15% |
| Catering | 7-8% |
| Food truck | 6-9% |
Among these types, bars lead with an average profit margin of 10-15%, while full-service restaurants lag at 3-5%. This indicates that bars can have profit margins up to four times greater than those of full-service establishments.
Calculating Average Restaurant Profit Margin
Calculating your restaurant’s profit margin involves several key steps. Follow this comprehensive guide:
-
Gather Financial Data. Collect your restaurant’s financial records, including total revenue and total expenses for the relevant period.
-
Calculate Total Revenue. Sum up income from food sales, beverage sales, catering, and any other revenue sources during that timeframe.
-
Determine Gross Profit. Subtract the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), which includes the costs of ingredients and materials, from your total revenue to find your gross profit. This reflects the funds earned after covering direct production costs.
-
Calculate Net Profit. Deduct your operating expenses (rent, utilities, wages, marketing, etc.) from your gross profit to arrive at your net profit, which is the amount remaining after all costs are covered.
-
Calculate Profit Margin. To find your profit margin, divide your net profit by total revenue and multiply by 100 to obtain a percentage. The formula is: Profit Margin (%) = (Net Profit / Total Revenue) x 100
Average Restaurant Profit Margin FAQs
-
Why are restaurant profit margins so low?
Restaurant profit margins are typically low due to high operational costs. The primary factors contributing to this include:
-
Inventory Costs. Restaurants must maintain a diverse inventory of food, which can be costly to store in compliance with health regulations. For instance, proper storage of meat requires freezers, and any unsold inventory can lead to significant losses.
-
Labor Costs. Staffing a restaurant involves various roles, each with different salary expectations. A restaurant’s operation relies on the presence of all staff members, from cooks to managers.
-
Rent Expenses. Whether large or small, rental costs can be substantial for restaurants, especially in high-traffic locations where rents tend to be elevated.
-
-
How can restaurants increase their profit margins?
There are several strategies to enhance restaurant profit margins, including waste reduction and menu optimization. Here are key recommendations:
-
Reduce Food Waste. Track inventory closely, ensure proper storage, and monitor the usage of ingredients to minimize waste.
-
Regular Expense Monitoring. As food costs fluctuate and guest counts vary, it’s vital to reassess expenses regularly.
-
Optimize Menus. Simplifying menus can reduce food waste, storage needs, and alleviate stress on staff. Focusing on fewer, high-quality offerings can lead to cost savings.
-
Train Staff for Upselling. Providing effective training and incentives can improve sales, reducing turnover and associated costs.
-
Enhance Takeout and Delivery Services. The rise in demand for takeout and delivery has persisted. Partnering with delivery apps or establishing your own delivery system can boost sales.
-
Stay Updated with Technology. Keeping up with advancements in restaurant technology is crucial for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
-
-
Which type of restaurant is most profitable?
Bars and fast-food restaurants are among the most profitable. Bars typically achieve profit margins of 10-15%, while fast-food establishments range from 6-9%.
Bars usually see higher profitability due to lower prep work for drinks and minimal storage requirements, complemented by streamlined food menus.
Fast-food restaurants also benefit from simplified menus and reduced staffing needs, allowing for an efficient operation.
-
What percentage of restaurants fail?
About 60% of restaurants fail within their first year of operation. This rate worsens over time, with around 80% closing within five years. Ultimately, this means that only 1 in 5 restaurants remain operational long-term.
Conclusion
The restaurant industry remains challenging, particularly for new entrepreneurs. For full-service restaurants, the average profit margin is between 3-5%, which is notably low compared to many other sectors. However, not all restaurant types are created equal.
For instance, bars and fast-food outlets enjoy higher average profit margins of 10-15% and 6-9%, respectively, largely due to their streamlined operations and reduced staffing needs.
Overall, while owning and managing a restaurant can be a risky endeavor, it is achievable with the right strategies and knowledge. As a restaurant owner, it’s vital to keep operations streamlined and regularly reassess your expenses, staffing, and technological tools.