20+ Eye-Opening Greenwashing Statistics [2026]
Greenwashing Research Summary. As consumers increasingly prioritize environmental sustainability in their purchasing decisions, many companies are claiming to offer greener products. However, not all of these claims are genuine. Some businesses misrepresent their environmental practices for marketing advantages.
If you’re a conscious consumer or a job seeker interested in greenwashing, you’re in the right place. We’ve compiled the latest greenwashing statistics, and our extensive research indicates:
-
68% of US executives acknowledge that their companies engage in greenwashing.
-
88% of Gen Z consumers express distrust in brands’ environmental, social, and governance (ESG) claims.
-
42% of corporate environmental claims made online are likely to be misleading or false.
-
58% of global C-suite leaders admit to engaging in greenwashing.
For further insights, we categorized the data into the following sections: Greenwashing Prevalence | Consequences | Consumer Opinions
Corporate Environmental Claims Statistics
Companies often make various claims regarding their positive environmental impact. However, many of these assertions lack credible evidence. Here are some examples of unsupported claims:
-
42% of greenwashing claims are exaggerated or false.
A European study found that 53.3% of environmental claims made in the EU are vague, misleading, or unsubstantiated.
-
In over 50% of cases, companies fail to provide factual support for their green initiatives.
Despite making assertions about their environmental efforts, more than half of companies cannot substantiate their claims.
-
60% of executives acknowledge that their organizations overstate sustainability practices.
While 85% believe customers are increasingly vocal about sustainability, many companies embellish their claims to meet these expectations, often without having effective sustainability plans in place.
-
59% of green claims made by leading European fashion brands are misleading.
Many brands misuse terms like “sustainable,” “eco-friendly,” and “responsible” without providing any evidence. The EU is likely to implement stricter regulations on green advertising if substantiating evidence is not presented.
-
40% of companies make green claims without evidence.
An example includes products claiming to be partially made from recycled materials without any proof to back such assertions.
Greenwashing Prevalence Statistics
Greenwashing is more widespread than many might realize. Under consumer pressure, numerous companies feel compelled to make sustainability claims without the evidence to support those assertions. Here are key statistics illustrating the scale of greenwashing:
-
72% of North American companies admit to engaging in corporate greenwashing.
This figure is 24% higher than the global average of 58%, indicating that greenwashing is particularly prevalent in North America.
-
43% of employees believe their company is involved in greenwashing.
Additionally, 83% feel that their company is not doing enough to pursue sustainability, indicating a significant gap between employee perceptions and executive actions.
-
Instances of greenwashing among global banks and financial services rose by 70% between 2022 and 2023.
Over half of these cases involved banks with ties to oil or fossil fuel industries, contradicting their sustainability claims.
-
80% of executives believe their companies are performing well in environmental sustainability.
Moreover, 86% think their efforts are impactful in promoting sustainability. However, many consumers feel that these efforts do not meet adequate standards, contributing to perceptions of greenwashing.
-
Only 36% of companies have evaluated the effectiveness of their sustainability programs.
While 85% claim they have initiated sustainability programs, only 36% have assessed their outcomes.
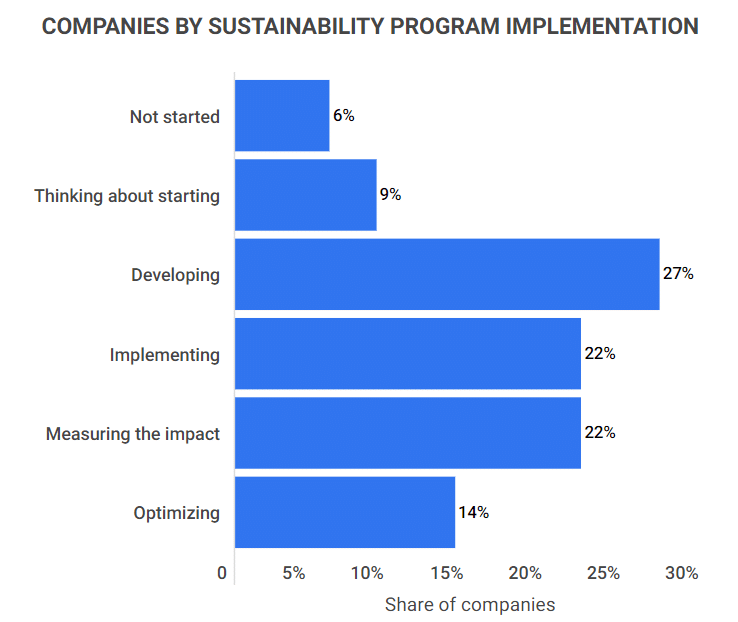
Companies by Sustainability Program Implementation
Status of Sustainability Program Share of Companies Have not started a program 6% Considering starting a program 9% Developing a program 27% Implementing a program 22% Measuring the impact of their program 22% Optimizing program based on measured outcomes 14%
Consequences of Being Caught Greenwashing
With many executives admitting to greenwashing, you may wonder what the repercussions are for being caught. Here’s what our research uncovered:
-
72% of corporate leaders believe that most organizations in their industry would be exposed for greenwashing if investigated thoroughly.
Ironically, while most executives think they are doing well in sustainability, they also believe their peers would be caught in similar practices if scrutinized.
-
Companies perceived to be greenwashing experience a 1.32% decline in customer satisfaction scores.
This drop translates to an average change of 0.032 units in net earnings and a 0.40 shift in ROI.
-
90% of the data required to assess sustainability performance is inaccessible to companies.
Given that only 36% of companies can evaluate their sustainability programs, the lack of available data is a significant barrier to understanding effectiveness.
-
The most significant greenwashing lawsuit resulted in Volkswagen being fined $33.3 billion.
In 2020, Volkswagen faced penalties for falsifying emissions reports, leading to numerous fines and financial settlements totaling billions.
-
60% of companies have emissions reduction targets.
However, only 81 major companies have disclosed credible climate transition plans.
Consumer Opinions on Greenwashing
Consumer awareness of sustainability has risen sharply. Many individuals feel disillusioned when promised sustainability initiatives turn out to be misleading. Here’s what consumers are saying:
-
38% of Americans believe companies should act responsibly towards the environment.
-
41% of Americans feel that companies are failing to reduce their carbon footprints effectively.
-
66% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for sustainable products.
-
55% of US consumers would cease purchasing from brands proven to make false sustainability claims.
-
75% of Gen Z consider product sustainability in their purchasing decisions, compared to 65% of Baby Boomers.
Importance of Sustainability When Purchasing a Product by Generation
| Generation | Share of Consumers Who Say Sustainability is a Factor |
|---|---|
| Gen Z | 75% |
| Millennials | 71% |
| Gen X | 73% |
| Baby Boomers | 65% |
Greenwashing FAQ
-
What is greenwashing?
Greenwashing is the practice of making false or misleading claims about the sustainability of a company’s products and operations. As environmental concerns grow among consumers, many companies have yet to develop effective sustainability strategies. Instead of being transparent, they promote unsubstantiated sustainability claims to attract customers and enhance their brand image.
-
What are examples of greenwashing?
There are several noteworthy instances of greenwashing. Here are the top three:
-
Lack of evidence supporting sustainability claims. For example, a tissue company might assert that it uses recycled materials without any proof to support that assertion.
-
Exaggerating environmental benefits beyond substantiated claims. For instance, a tissue company might use some recycled materials but advertises the process as being more sustainable than it truly is, which constitutes greenwashing.
-
Promoting products as environmentally friendly while sourcing materials from unsustainable suppliers. Many electric vehicle manufacturers promote their cars’ sustainability while sourcing metals for batteries from unsustainable sources.
-
-
Which companies engage in greenwashing?
Many prominent companies, including Volkswagen and Starbucks, have been accused of greenwashing. Volkswagen, in particular, has incurred over $33 billion in fines due to greenwashing practices.
Other companies cited include:
-
BP
-
ExxonMobil
-
Nestlé
-
Coca-Cola
-
IKEA
-
Poland Spring
-
H&M
-
JP Morgan, Citibank, and Bank of America
-
McDonald’s
-
Walmart
And many others.
-
-
What percentage of companies engage in greenwashing?
58% of companies globally are involved in greenwashing. This figure is even higher in North America, where 72% of companies are reported to engage in such practices.
-
In which industries is greenwashing most prevalent?
Greenwashing is especially common in the fashion industry. Faced with issues related to fast fashion and labor practices, many brands aim to enhance their social and environmental standards, yet greenwashing exacerbates the problem.
Other industries with notable greenwashing rates include:
-
Automotive
-
Food and Beverage
-
Banking and Finance
-
Energy
-
Conclusion
As consumers increasingly scrutinize the environmental impact of businesses, many companies strive to present themselves as environmentally responsible. Unfortunately, inadequate infrastructure and investment in genuine sustainability efforts lead many to make misleading claims for enhanced brand reputation instead of committing to authentic sustainability initiatives.
A striking 72% of North American and 58% of global companies admit to engaging in greenwashing, resulting in negative financial repercussions. For instance, Volkswagen faced a staggering $33 billion fine in 2020 due to their greenwashing practices.
With 55% of consumers indicating they would stop purchasing from brands caught greenwashing, it is in the best interest of companies to embrace transparency and invest in real sustainability programs for the sake of both the planet and long-term profitability.
References
-
LinkedIn – 68% of CEOs admit their businesses are guilty of greenwashing.
-
European Commission – Consumer protection: enabling sustainable choices and ending greenwashing
-
Reuters – Banks behind 70% jump in greenwashing incidents in 2023 -report
-
Google Cloud – Report: What it will take for CEOs to fund a sustainable transformation
-
Circularise – Greenwashing lawsuits in businesses: Notable cases and consequences (Part 2)
-
WEF – Gen Z cares about sustainability more than anyone else – and is starting to make others feel the same







